Salicylic Acid (Lab Grade)
Key Points
- Chemical Formula: Salicylic acid has the chemical formula C₇H₆O₃. It is a beta hydroxy acid (BHA) and a phenolic acid derived from the metabolism of salicin.
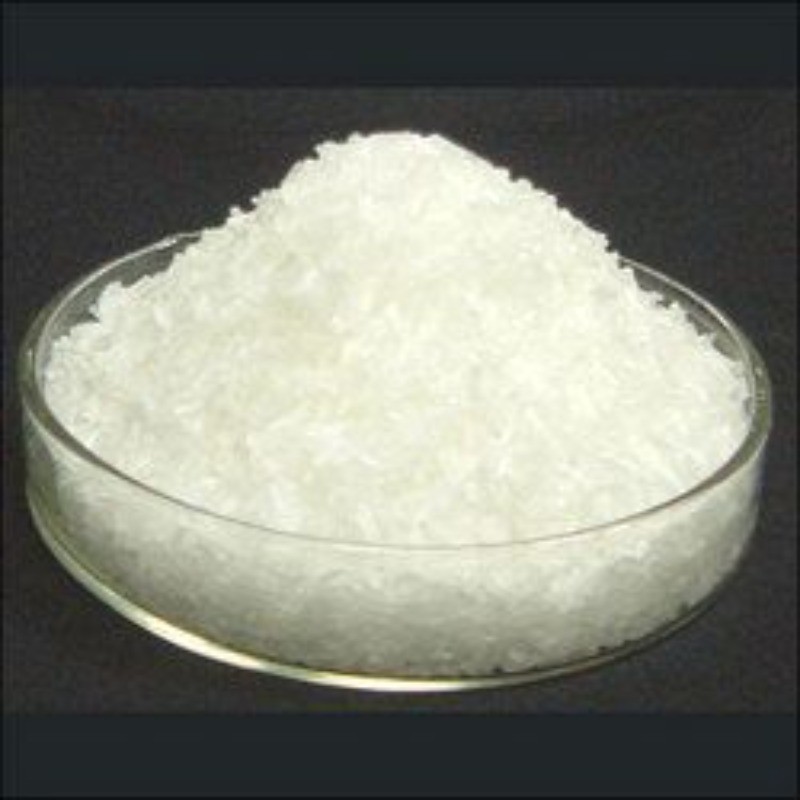
- Physical Appearance: It is typically a white, crystalline powder or colorless crystals with a slight odor.
- Solubility: Salicylic acid is sparingly soluble in water but highly soluble in ethanol and ether, making it versatile for various laboratory applications.
- Purity: Lab-grade salicylic acid is of high purity, suitable for precise analytical and experimental purposes, with minimal impurities.
- Melting Point: It has a melting point of around 158-161°C, making it stable under standard laboratory conditions.
- Acidic Properties: Salicylic acid is a weak acid with both antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties, commonly used in chemistry and pharmacology labs.
Uses of Salicylic Acid (Lab Grade)
- Chemical Synthesis: Used as a precursor in the synthesis of various organic compounds, including aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid).
- Analytical Chemistry: Employed in analytical procedures to detect and quantify metals like iron, with which it forms a colored complex.
- Pharmaceutical Research: Widely used in the development and testing of skincare and pharmaceutical products, particularly for treating acne and other skin conditions.
- Preservative: Acts as a preservative in some laboratory formulations and products due to its antimicrobial properties.
- pH Adjustment: Utilized to adjust the pH of solutions in chemical and biological experiments, especially when a weak acid is required.
- Study of Reactions: Used in educational settings to demonstrate reactions involving carboxylic acids, esterification, and related organic chemistry topics.
Precautions When Using Salicylic Acid (Lab Grade)
- Skin and Eye Irritation: Salicylic acid can cause irritation to the skin and eyes. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats.
- Avoid Inhalation: Inhalation of salicylic acid dust can irritate the respiratory system. Work in a well-ventilated area or use a fume hood and wear a mask if necessary.
- Handling and Storage: Store in a tightly sealed container in a cool, dry place, away from incompatible substances such as strong oxidizers and acids. Protect from moisture to prevent degradation.
- Spill Management: In case of a spill, avoid creating dust and clean up using methods that minimize dust generation, such as wet wiping or using a vacuum with a HEPA filter.
- First Aid Measures: In case of skin or eye contact, rinse thoroughly with water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention if irritation persists. If inhaled, move to fresh air and seek medical advice if symptoms develop.
- Disposal: Dispose of salicylic acid according to local regulations. Do not pour it down the drain. Collect and label waste for proper disposal through a hazardous waste management system.
If you'd like to know more about this chemical or need any analysis report regarding this chemical then contact us: support@echem.com.bd.
Salicylic Acid (Lab Grade)
Formula: C7H6O3
Formula Wt.: 138.13
CAS: 69-72-7
Characteristic: White
- Storage Code: Blue—toxic; store separately in a secured area



 Health & Beauty
Health & Beauty


.png) Art & Painting
Art & Painting Hot Deals
Hot Deals

.png)


















Login To Comment